Vue组件通信方式
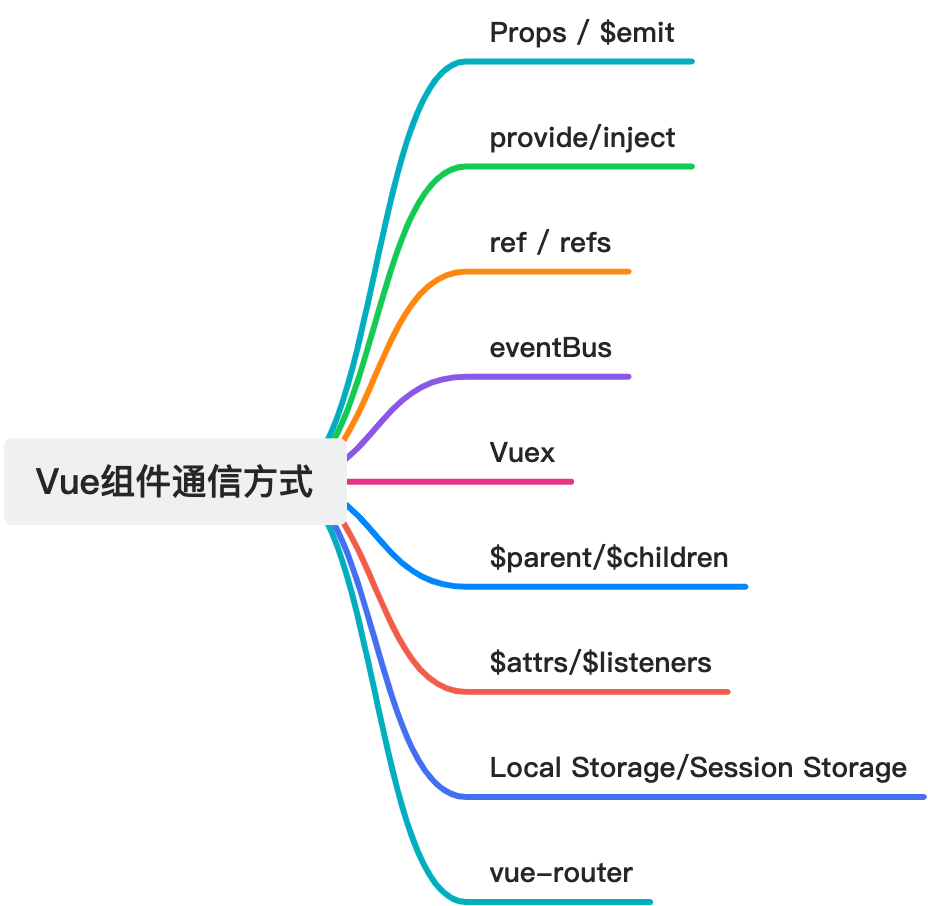
Props / $emit
Props用于父子组件通信:当一个组件需要向它的子组件传递数据时;$emit用于子父组件通信:当子组件需要向父组件发送消息或触发事件时。
父组件:
<template>
<ChildComponent :message="parentMessage" @customEvent="handleCustomEvent" />
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: {
ChildComponent
},
data() {
return {
parentMessage: 'Hello from parent!'
};
},
methods: {
handleCustomEvent(payload) {
console.log('Received from child:', payload);
}
}
};
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div>
<div>
{{ message }}
</div>
<button @click="sendDataToParent">Send Data</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['message'],
methods: {
sendDataToParent() {
this.$emit('customEvent', 'Data sent from child');
}
}
};
</script>Props 和 $emit 是 Vue 中常用的父子组件通信方式,分别用于从父组件向子组件传递数据和从子组件向父组件触发事件。这种方式是 Vue 中最常见和推荐的通信方式之一。
provide/inject
当你需要在组件树中的祖先组件向子孙组件传递数据时,可以使用 provide 和 inject。这种方式不同于传统的父子组件通信,它允许你在一个祖先组件中提供数据,然后在后代组件中注入并使用这些数据。
使用场景:
- 当你有一个组件层次结构,需要在多个后代组件中共享相同的数据,例如主题、语言设置等。
- 当你想要在深层次的子组件中访问一些全局数据,而不必通过每个中间组件进行传递。
祖先组件:
<template>
<div>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: {
ChildComponent
},
provide() {
return {
sharedMessage: 'This message is shared!'
};
}
};
</script>后代组件:
<template>
<div>{{ sharedMessage }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inject: ['sharedMessage']
};
</script>注意事项
inject会创建一个响应式的绑定,但它的更新是从父组件到子孙组件的单向流动,这意味着如果你在子孙组件中修改了inject的值,不会影响到祖先组件的数据。- 虽然
provide和inject提供了一种组件之间共享数据的方式,但也要谨慎使用,避免滥用,因为它可能导致组件之间的耦合增加
ref / refs
ref 和 refs 是 Vue 中用于获取对组件或 DOM 元素的引用的机制。通过使用 ref 属性,你可以在父组件中获取对子组件的引用,然后通过 $refs 对象访问这些引用。
使用场景:
- 当你需要在父组件中调用子组件的方法或访问子组件的属性。
- 当你需要直接操作子组件关联的 DOM 元素。
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<ChildComponent ref="childComponentRef" />
<button @click="callChildMethod">Call Child Method</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: {
ChildComponent
},
methods: {
callChildMethod() {
this.$refs.childComponentRef.childMethod();
}
}
};
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div>Child Component</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
childMethod() {
console.log('Child method called');
}
}
};
</script>注意事项
- 使用
ref和$refs需要谨慎,因为它可能导致你绕过了 Vue 的响应式数据流,增加了组件之间的耦合。
eventBus
EventBus 是一种 Vue 中用于实现组件间通信的简单的事件总线模式。它是通过创建一个空的 Vue 实例,作为中央事件管理器,用于在组件之间传递事件和数据。尽管它是一种简单的通信方式,但在一些简单的应用场景中是有效的。
使用场景:
- 当多个组件之间需要进行非父子关系的通信时,或者当组件之间的层级结构较复杂时。
- 当你有多个组件,但只有几个之间需要共享数据或响应事件。
创建 EventBus 实例:
// EventBus.js
import Vue from 'vue';
export const EventBus = new Vue();组件中使用
<template>
<div>
<button @click="sendMessage">Send Message</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { EventBus } from './EventBus.js';
export default {
methods: {
sendMessage() {
EventBus.$emit('messageSent', 'Hello from EventBus!');
}
}
};
</script>在另一个组件中监听并接收事件:
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ receivedMessage }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { EventBus } from './EventBus.js';
export default {
data() {
return {
receivedMessage: ''
};
},
created() {
EventBus.$on('messageSent', message => {
this.receivedMessage = message;
});
}
};
</script>注意事项
- EventBus 是一种全局事件总线,过度使用可能导致代码难以维护,应谨慎使用。
Vuex
Vuex 是 Vue.js 的官方状态管理库,用于管理应用程序的状态(数据)。它提供了一种集中式的状态管理模式,使得多个组件可以共享和操作同一个状态,从而实现更复杂的数据流控制和组件通信。
使用场景:
- 当多个组件需要访问相同的数据或状态时。
- 当你的应用程序的状态逻辑变得复杂,需要更好地组织和管理数据流。
- 当你需要在组件之间进行复杂的异步操作和数据操作时。
- 当你想要实现中央化的数据管理,而不是在组件之间传递数据。
设置 Vuex Store:
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
message: 'Hello from Vuex!'
},
mutations: {
updateMessage(state, newMessage) {
state.message = newMessage;
}
},
getters: {
getMessage: state => state.message
}
});在组件中使用 Vuex:
<template>
<div>
<p>Message from Vuex: {{ message }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['message'])
}
};
</script>在其他组件中使用 Vuex:
<template>
<div>
<p>Message from Vuex in another component: {{ message }}</p>
<button @click="updateMessage">Update Message</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['message'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['updateMessage'])
}
};
</script>$parent/$children
$parent 和 $children 是 Vue 实例提供的两个属性,用于在组件内部访问其父组件和子组件。
使用场景:
- 一个组件中访问其直接父组件或子组件的属性或方法时
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<ChildComponent />
{{ parentMessage }}
<button @click="getChild">getChild</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: {
ChildComponent
},
data() {
return {
parentMessage: 'Hello from parent!'
};
},
methods : {
getChild(){
console.log(this.$children[0])
}
}
};
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="setParent">setParent</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'ChildComponent',
methods: {
setParent() {
// 通过$parent我们可以获取父组件实例,并设置值
this.$parent.parentMessage = 'Hello from ChildComponent!'
}
}
};
</script>注意事项
- 使用 $parent 和 $children 会造成高度耦合,不推荐过度使用
- $parent 和 $children 无法跨级访问,只能访问直接的父子关系
- 在Vue3中无法访问$children,需要使用 refs
$attrs/$listeners
$attrs 和 $listeners 是 Vue 中用于处理组件属性和事件的特殊属性。它们主要用于在具有嵌套关系的组件中传递属性和事件。
使用场景:
- 通常在高阶组件(Higher Order Component,HOC)或其他需要将属性和事件传递到子组件的场景中使用。
父组件:
<template>
<ChildComponent v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"/>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: {
ChildComponent
}
};
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div>
{{ propFromParent }}
<button @click="$emit('custom-event')">Trigger Custom Event</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
propFromParent: String
}
};
</script>Local Storage/Session Storage
LoLocalStorage 和 SessionStorage 可以用来在 Vue 组件之间共享数据,原理是不同组件实例都可以访问同一个本地存储。
使用LocalStorage 在组件A中:
// 写入数据
localStorage.setItem('name', 'John')
// 读取数据
const name = localStorage.getItem('name')在组件B中:
// 读取组件A写入的数据
const name = localStorage.getItem('name')使用SessionStorage 同理,使用sessionStorage: 组件A:
sessionStorage.setItem('age', 20)组件B:
const age = sessionStorage.getItem('age')LocalStorage的数据会长期保存,SessionStorage的数据只存在于当前会话,刷新后清空。
注意事项
- 不能很方便地做数据监听,需要手动watch
- 存储容量较小(仅5MB左右)
- LocalStorage/SessionStorage只适合用于非核心的组件间数据共享,不适合复杂应用状态管理
vue-router
严格来说,vue-router通过路由传参实现的不完全是组件之间的通信,而是通过路由参数在不同路由(组件)之间传递数据。但确实可以把它看作一个间接的组件通信方式。 组件A
// 传递userId参数
this.$router.push({
name: 'user',
params: {
userId: 1234
}
})在组件B中(user组件)
// 接收userId参数
const userId = this.$route.params.userId通过这种方式,可以在A组件和B组件之间传递参数,实现了某种形式的组件间通信。
注意事项
- 组件之间存在依赖关系,不够纯粹。